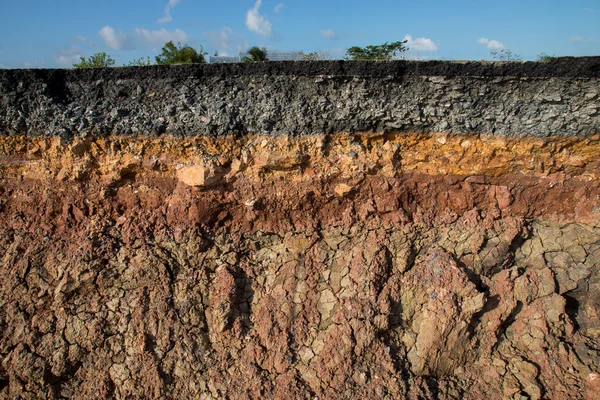
Soil is one of the most vital resources on the planet. Soil is a thin layer covering the earth’s surface, made of organic material. The minerals, gases, liquids, and living things that makeup soil are all necessary for the existence of life.
We humans, animals, trees, and plants exist because of the soil. Without the soil, there is no life on earth. It is only because of the soil that we are able to grow food grains. Soil is essential for containing water, minerals, and nutrients for plant growth.
In today’s time, the fertility of the soil is rapidly decreasing because there has been a huge decrease in the production of food grains.
What is Soil Degradation?
The term “soil degradation” describes the processes by which soil loses quality and becomes less suitable for a particular activity, such as crop cultivation. The loss of fertile land owing to urbanisation, overgrazing, and unsustainable farming practices, as well as long-term climate changes, are all factors that contribute to soil degradation. These factors include agricultural, industrial, and commercial pollutants. In simple terms, Soil degradation means loss of soil quality brought on by chemical, physical, and biological factors.
What is Soil Erosion?
The soil particles are loosening or being washed away in valleys, oceans, rivers, streams, or remote areas due to Human activities like agriculture and deforestation. This process is known as Soil Erosion. Continuous soil deterioration can happen slowly or rapidly, depending on the situation. Continual topsoil loss, ecological harm, soil collapse, etc., are the outcomes
What are the main causes of Soil Erosion?
-
Soil Erosion by Wind
Soil is moved by the wind’s force in a natural process called wind erosion. The tiny soil particles are swept away by the wind to distant places in dry weather or semi-arid regions. In desert and semi-desert environments where strong gusts are widespread, wind erosion is quite common.
-
Soil Erosion by Water
Raindrop impact and water flow are the two primary factors that produce water erosion. Raindrops have the power to disintegrate soil aggregates and move soil over short distances. After that, these separated particles are carried downhill by moving water. The kinetic energy of the water increases with a particle size as it is carried. The size of the moving particles increases with water depth. These particles disperse from the field and wind up in rivers and other bodies of water.
-
Overgrazing by Farming Cattle
Cattle overgrazing decreases plant cover and prioritizes eradicating the most attractive fodder species. This causes the soil to erode more quickly and have less fertility since it exposes the area to unwelcome plants, shrubs, and trees.
-
Deforestation
Deforestation is the process of systematically removing trees from forests (or other locations) to provide space for human activity. Since it can result in soil erosion, habitat destruction, biodiversity loss, and disturbance of the water cycle, it poses a serious threat to the ecosystem. Deforestation is another factor contributing to climate change and global warming. Since it can result in soil erosion, habitat destruction, biodiversity loss, and disturbance of the water cycle, it poses a serious threat to the ecosystem. Deforestation is another factor contributing to climate change and global warming. Since it can result in soil erosion, habitat destruction, biodiversity loss, and disturbance of the water cycle, it poses a serious threat to the ecosystem. Deforestation is another factor contributing to climate change and global warming.
What are the Impacts of Soil Erosion?
-
Loss of Arable Land for Agriculture
Any area that can be utilised to cultivate crops is considered arable land. Many of the techniques utilised to cultivate those crops have the potential to destroy the soil’s agronomic qualities and cause topsoil loss.
-
Chocking of Waterways
Pesticides and fertilizers used on fields are washed into streams and other bodies of water together with soil that has eroded from the land. The freshwater and marine environments, as well as the nearby communities that depend on them, may be harmed by this sedimentation and pollution.
-
AN INCREASE IN FLOODS
Crop fields and pastures are frequently created on land that was previously a forest or another type of natural landscape, including floodplains and wetlands. Since the modified terrain is less able to absorb water, flooding is more frequent. There are ways to maintain and restore wetlands as well as increase soil’s ability to hold water.
Why Is It Important to Prevent Land and Soil Degradation?
The soil gives the earth a lot of vitality. In the absence of soil boundaries at the roots, there would be:
- No plants
- with no greenery or trees
- No food for both humans or animals.
Soil preservation is crucial to ensuring human nourishment and development. Let’s move in the direction of the elements or strategies that can lessen erosion’s consequences.
Factors to Curb the Effects of Land Degradation & Soil Erosion
-
Crop Rotation/Mixed Farming
Crop rotation helps to the creation of a biodiverse soil, which lowers the risk of pests infecting organisms that are rooted in the soil and minimises the need for pesticides.
Crop rotation reduces the likelihood that herbs will become weeds that need to be removed, hence lowering the demand for pesticides.
Crop rotation helps in obtaining a strong soil structure, high organic matter levels, and enough water supply, especially when combined with conservation tillage, leading to a higher yield.
-
Afforestation
Reforestation or Afforestation is the planting of trees on previously deforested land. Afforestation is the conversion of abandoned and degraded agricultural lands into woods.
-
Terrace Farming
Terrace farming is the method of creating flat areas out of hilly or mountainous terrain in order to grow crops.
Crops are grown on the sides of hills or mountains by planting them on graduated terraces that have been cut into the slope.
-
Using Quality Tractor & Farming Implements
Sometimes, incorrect or excessive usage of tractors , mini tractors and farming equipment leads to soil erosion. The soil may become dry and exposed to wind or flowing water if there is maximum tillage or ploughing.
-
Development of Shelterbelts/Windbelts
Shelterbelts are rows of trees or bushes planted for crop protection against wind, whereas windbreaks are such structures that break the wind flow and reduce wind speed.
They stop soil erosion, stop the spread of the desert, and shield inhabited and agricultural areas from dust storms.