Are you one of those couples trying to conceive desperately and failing to understand why you are unable to? Consult Dr. Mohit Saraogi, an IVF specialist, to know why.
So far, we have read up on so many articles trying to figure out infertility. You may also have. But reading up articles will not help you figure out the cause.
We have read about the reasons for infertility like autoimmune disorders, male infertility, and more. But today, you will get to know the most random reason for not being able to conceive. – Genital Tuberculosis.
That is why being able to tell your gynecologist about your medical history accurately is so crucial.
Dr. Mohit Saraogi educates us through this article about the implications of genital Tuberculosis and infertility.
Dr. Saraogi has founded his best IVF hospital in Mumbai as Saraogi Hospital and has provided the service to several aspiring couples to be proud parents of a bundle of joy.
But treating infertility is challenging since it involves treating the cause of infertility, and diagnosis comes only with experience.
To know more about Saraogi hospital and Dr. Saraogi himself, click here.
In the meanwhile, read up to know more about genital Tuberculosis.
What is Tuberculosis of the Genitals?
Tuberculosis is a proliferating disease in upcoming nations like India. Tuberculosis of the genital tract occurs quite generally following tuberculosis infection elsewhere in the body and primarily increases via the bloodstream to the genitals. When the contagion attacks the reproductive system, i.eThe genital path usually targets the fallopian tubes and the uterus. Women between 20 – 40 years of age are the most susceptible to it.
Genital Tuberculosis can be a silent disease, and a high degree of suspicion is needed for proper diagnosis and treatment. A consultation at one of the best IVF Hospitals in Mumbai, Saraogi Hospital and Iris IVF center, will help you come to a proper diagnosis of your condition.
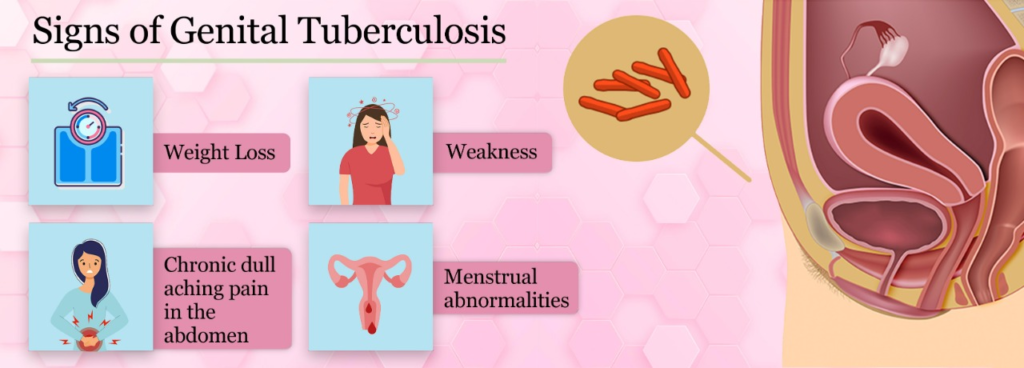
Signs of genital Tuberculosis.
The most common presenting symptom is infertility, i.e., the inability to conceive.
Symptoms may include
- weight loss,
- weakness,
- chronic dull aching pain in the abdomen
- and menstrual abnormalities.
How does genital Tuberculosis affect the reproductive system?
The fallopian tubes are involved in 80-90% of the cases. Small nodules of tubercular material are found on the surface of the tubes initially; the infection invades the tubes and affects the internal surface of the tubes. Pus collection occurs within the tubes blocking them either entirely or partially. If the block is partial, it can cause ectopic pregnancy, leading to severe internal bleeding if not diagnosed well in time. Once infection occurs within the tubes, the internal lining of the tubes gets scarred, blocked, and becomes non-functional leading to infertility.
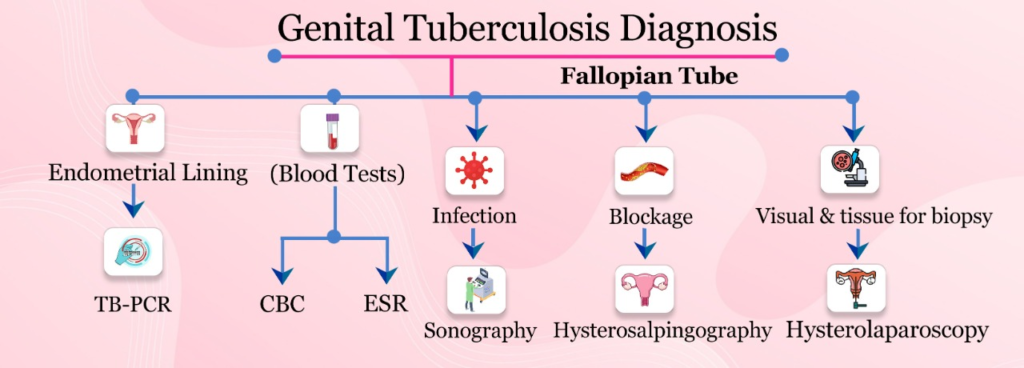
How is genital Tuberculosis diagnosed?
Various methods are available to test for tubal involvement, such as Sonography, Hysterosalpingography, and Hysterolaparoscopy.
- Sonography helps diagnose infection in the fallopian tubes,
- hysterosalpingography helps diagnose blockage in the fallopian tubes,
- and laparoscopy is direct visualization of the tubes, allowing us to take a tissue sample from the suspected lacerations.
- TB-PCR from the endometrial lining is also one of the essential tests for the identification of Tuberculosis. Of course CBC and ESR also assists in detection.
What are the risk factors for genital Tuberculosis?
If anti-TB medicines are started in the initial stages of the disease, then the permanent damage may be avoided. But if by the time the cause is identified the genitals are already impaired, then the best treatment is to resort to assisted reproduction.
Conclusion.
If you have not yet tried to get pregnant, and if you do not have the symptoms mentioned above, please visit a Dr. Mohit Saraogi to discuss and plan a pregnancy. If you do not get pregnant within 6 months, then you may need to undergo various tests to know the cause. But if you do show the signs of TB it is best to get tested for GTB to rule out the complication.















